Supporting Children with Autism in Developing Daily Living Skills through ABA Therapy

Introduction
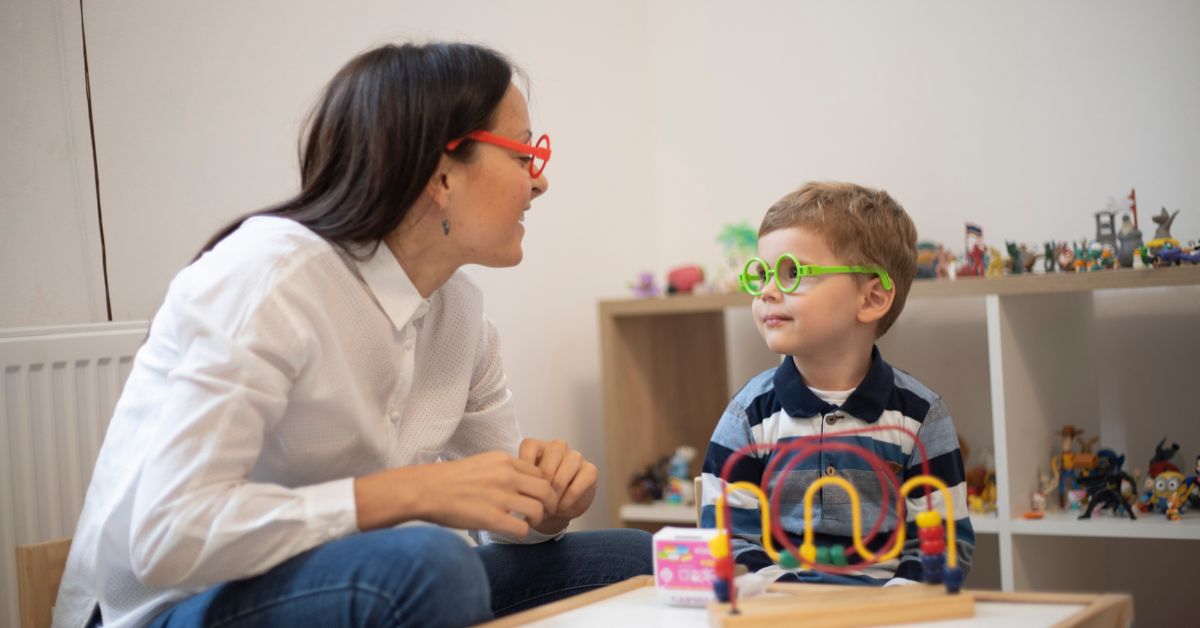
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a pivotal tool in aiding children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) to acquire essential daily living skills. With a foundation grounded in scientific principles and decades of application, ABA therapy offers tailored strategies that significantly impact the independence and confidence of autistic children. This article explores the methodologies, parental involvement, and evidence-based practices that make ABA therapy a transformative approach for developing crucial life skills.
Understanding ABA Therapy and Its Impact

What are the methods and benefits of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in developing daily living skills?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is an evidence-based intervention specifically designed to assist children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in mastering essential daily living skills. This comprehensive approach employs a variety of techniques, including:
- Positive Reinforcement: Encourages desirable behaviors by providing rewards, thus enhancing motivation.
- Task Analysis: Breaks down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps, making learning more digestible.
- Prompting Techniques: Involves providing guidance through physical or verbal cues, gradually reduced as the child gains proficiency.
- Visual Supports: Utilizes aids like pictures or social stories to help children understand and execute tasks effectively.
Through these methods, children learn crucial life skills such as grooming, cooking, and personal hygiene. For example, teaching how to brush teeth can be segmented into simple steps—gathering the toothbrush, applying toothpaste, brushing, and rinsing. Each step is practiced until the child can perform it independently.
Benefits of ABA for Daily Living Skills
The benefits of ABA therapy extend beyond the acquisition of daily living skills. Here are some highlighted advantages:
- Enhanced Independence: Children acquire skills that allow them to engage more fully in family and community activities.
- Personalized Interventions: Strategies tailored to individual needs ensure optimal learning experiences, promoting self-growth.
- Increased Confidence: Mastering skills boosts self-esteem, allowing children to face everyday challenges with assurance.
- Integration into Daily Life: By applying learned skills both at home and in varied settings, children can generalize their abilities, leading to more consistent performance.
Overall, ABA therapy systematically promotes the mastery of daily living skills, supporting children as they transition toward greater autonomy and independence.
The Importance of Early Intervention

Benefits of Early Initiation
Early intervention through Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy can be transformative for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Commencing ABA therapy at a young age allows children to harness their potential by addressing communication, social skills, and daily living skills early on. Research indicates that children who begin therapy before age three experience more favorable developmental trajectories, particularly in daily living skills (DLS).
When parents are actively involved in the intervention, improvements can be significant. One particular study shows that engaging in more than 20 hours of parent-implemented intervention before age three leads to better DLS outcomes. These critical early years provide a window of opportunity for establishing routines and teaching essential skills in a supportive environment.
Long-term Outcomes of ABA
The long-term impacts of early ABA intervention are noteworthy. Children who initiate therapy early tend to demonstrate enhanced cognitive, academic, and social capabilities as they grow older. They are more likely to achieve greater independence in daily living tasks, reducing the need for constant supervision and support.
Moreover, the emphasis on personalized approaches in ABA ensures that interventions are tailored to each child's specific needs, fostering resilience and adaptability in various real-life situations. Overall, early ABA intervention not only equips children with essential skills but also contributes substantially to their overall well-being and quality of life.
Parental Involvement in ABA Therapy

What role does parental involvement play in the effectiveness of ABA therapy for children with autism?
Parental involvement plays a fundamental role in the effectiveness of ABA therapy for children with autism. It is consistently recognized as the most critical factor for success in early intervention programs. When parents are trained in ABA techniques, they can actively participate in their child’s therapy, significantly enhancing the child’s learning and skill development. Given that children spend most of their time with their parents, this involvement promotes the generalization of learned behaviors to home and community environments.
Research indicates that parent-led or parent-mediated interventions have notable benefits. For instance, they can improve parental self-efficacy, reduce stress, and ultimately lead to more positive therapeutic outcomes for both the child and the parent. When parents understand and implement ABA strategies, they not only support their child's learning but also reinforce essential daily living skills in familiar settings.
Effective collaboration between parents and professionals is key to maximizing the benefits of ABA therapy. This partnership results in improved developmental skills and enhances the overall quality of life for families. Such involvement fosters a nurturing environment where children with autism can thrive, making daily living skills more accessible and achievable.
Implementing ABA Strategies at Home

How can parents implement ABA strategies at home to assist autistic children in learning essential daily living skills?
Parents play a vital role in the implementation of ABA strategies at home, enhancing their child's ability to learn essential daily living skills. Creating a structured environment is key. Clear, achievable goals should be established along with consistent routines to help children feel secure and focused.
Incorporating techniques like modeling and reinforcement is essential. For instance, parents can demonstrate tasks such as personal hygiene routines or meal preparation. Positive reinforcement, such as offering praise or rewards for successfully completed tasks, encourages children to repeat these desired behaviors.
Using visual supports significantly aids learning as well. Visual aids like picture schedules or step-by-step images assist children in understanding daily tasks better. Engaging children in relatable activities, such as sorting household items or matching colors, helps reinforce learning in an enjoyable way.
Collaboration with ABA professionals
Collaboration with ABA professionals offers invaluable support in customizing approaches to meet specific child needs. Parents can work with professionals to develop tailored strategies that align with their child's individual goals. Continuous monitoring and adjusting strategies based on the child's progress is a critical component of this partnership.
Additionally, parents should feel empowered to seek guidance on utilizing structured activities at home that echo techniques used during therapy. This coordination between home and professional settings fosters a holistic approach that significantly boosts the child's ability to develop crucial skills necessary for independent living.
Evidence-Based Practices in ABA
What are evidence-based practices for enhancing daily living skills in children with autism through ABA therapy?
Evidence-based practices in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy are essential for enhancing daily living skills among children with autism. These practices focus on individualized intervention plans that cater to each child’s unique needs, promoting effective learning and skill acquisition.
Effective Techniques in ABA Therapy
Several key techniques are employed within ABA to support daily living skills:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): This method breaks down tasks into smaller, manageable components, providing structured learning opportunities.
- Natural Environment Training (NET): This approach emphasizes teaching skills in real-life settings, allowing children to learn in contexts they will actually use these skills.
- Task Analysis: This technique simplifies complex tasks into smaller steps, ensuring children can master each step before moving to the next, which builds confidence.
Communication skills are also a focal point. Techniques such as Functional Communication Training (FCT) and the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS) are particularly effective for enhancing communication abilities among children with autism, enabling them to express their needs and interact more successfully.
Visual supports, including Social Stories and Video Modeling, play an important role in helping children understand social norms and daily routines. These strategies provide clear, visual guidance that can ease the learning process.
Empowering Families for Success
To maximize the benefits of these interventions, training programs for parents and caregivers are vital. They help family members reinforce learned skills at home, providing continuous support and promoting further development.
Research consistently backs these methods, highlighting their effectiveness in improving daily living skills, social behavior, and overall adaptability for children with autism. This evidence illustrates the importance of tailoring ABA interventions to effectively address the individual needs of each child.
Promoting Independence Through ABA Techniques
What are the best strategies and techniques in ABA to promote independence in self-care routines for autistic children?
To foster independence in self-care routines among autistic children, ABA therapy employs various effective strategies. A primary method is breaking complex tasks into manageable steps using task analysis. This approach ensures that each step is clearly defined and taught sequentially, allowing the child to master one aspect before moving on to the next.
Visual aids, such as schedules or pictorial task lists, play a crucial role in supporting transitions and aiding decision-making. These tools help children visualize the steps necessary for tasks like brushing teeth or dressing, reinforcing their learning in a clear and structured way.
Incorporating Alternative/Augmentative Communication (AAC) tools can enhance a child’s ability to express preferences and emotions during self-care activities. This participation not only builds confidence but also motivates practice through positive reinforcement. For instance, providing tokens or rewards for completing self-care tasks encourages children to engage more actively.
Additionally, teaching children to request breaks as they work and involving them in household chores serves to build responsibility and practical life skills. As children gain competence, it’s important to adapt routines to meet their evolving needs, including introducing vocational skills during adolescence to prepare them for future independence.
Overall, the focus on generalizing learned skills across diverse contexts ensures that children can apply what they’ve mastered in real-life situations, enriching their daily living capabilities and personal autonomy.
Tailoring ABA Therapy to Individual Needs

Customization of therapy
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is uniquely adaptable, focusing on the individual needs of each child with autism. By evaluating and targeting socially significant behaviors, such as communication and daily living skills, therapists employ personalized approaches to create effective learning environments. This customization is essential in ensuring that the therapy aligns with the child’s specific goals and challenges.
Therapists assess each child's strengths and weaknesses through behavioral assessments, informing tailored strategies that promote skill acquisition. By understanding the child's preferred learning styles—whether through visual aids, hands-on activities, or contextual teaching—therapists can enhance the educational process.
Techniques for specific challenges
Several techniques are integral to the success of ABA therapy in addressing particular challenges. Here are a few:
| Technique | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Discrete Trial Training (DTT) | Focuses on breaking skills into small, manageable steps | Ideal for teaching tasks like meal preparation or personal care. |
| Pivotal Response Training (PRT) | Emphasizes key areas for development, including motivation | Supports social skills and communication improvements. |
| Visual Supports | Uses pictures and charts to assist understanding | Aids in task completion and social interactions. |
| Role-Playing | Engages children in social scenarios | Builds confidence and practice in real-life interactions. |
Through these methods, ABA not only teaches essential skills but also fosters independence and adaptability, critical for children with autism as they navigate daily life.
Visual Aids and Communication Tools in ABA
Role of visual supports
Visual aids are an essential component in Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, especially for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). These tools can include pictures, schedules, and charts that visually represent tasks or social cues. Using visual supports helps children understand complex concepts by breaking down information into simpler, more digestible formats. For instance, a picture schedule can clarify the steps involved in daily routines, making transitions smoother and fostering independence.
Enhancing communication skills
A significant aim of ABA therapy is to improve communication skills. Tools like the Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS) facilitate interactions by allowing non-verbal children to express their needs and desires visually. These methods not only reinforce language development but also help children navigate social situations. By incorporating visual supports into everyday interactions, ABA therapy strengthens the foundations of communication, making it easier for children to engage with peers and adults alike.
| Visual Aid Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Picture schedules | Clarifies routines and transitions | Daily morning schedule |
| PECS (Picture Exchange Communication System) | Aids in verbal communication for non-verbal children | Symbols for 'food', 'drink', 'play' |
| Social stories | Teaches social norms and cues | Story about sharing with friends |
The Bigger Picture: Future Implications of ABA
Long-term Benefits
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is not just a short-term solution; it lays a foundation for long-term success. Research shows that early initiation of ABA serves as a predictor for improved cognitive, academic, adaptive, and social skills. Children who engage in ABA therapy often become more independent, effectively transitioning into adulthood with greater life skills.
The longitudinal studies following individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) reveal that those who receive tailored ABA interventions demonstrate significant progress in daily living skills, which tend to lag behind their neurotypical peers. As these individuals grow, positive trajectories in areas like job readiness and personal care emerge, showcasing the lasting impact of early therapeutic engagement.
Impact on Family Dynamics
Parent and caregiver involvement in ABA therapy enhances not just the child's development but also the overall family dynamic. Training parents in effective strategies empowers them to support their children better, leading to improved relationships and understanding within the family.
When caregivers are equipped with tools to reinforce learning in daily settings, such as home and school, it generates a cohesive approach that promotes unity and boosts the child's chances for success. Moreover, fostering independence in children reduces stress for families, allowing them to focus on creating a nurturing environment that encourages growth and development.
Conclusion
ABA therapy stands as a cornerstone in enhancing the daily living skills of children with autism, driving their journey toward greater independence. By focusing on tailored strategies and involving parents as active participants, this therapy offers sustainable benefits both to the children and their families. With continuous research and adaptation, ABA therapy promises an evolving roadmap for empowering autistic children in their daily lives and beyond.
References
- Exploring the Importance of ABA Therapy for Autism
- Ways ABA Therapy Can Help Improve Skills For Life
- Daily living skills in individuals with autism spectrum disorder from 2 ...
- How ABA Therapy Can Help Children with Autism Thrive
- Life Skills to Teach a Child With Autism - MySpot
- How to Build Independent Living Skills in Your Child With Autism
- 8 Ways to Boost Social Skills in Kids with Autism
- ABA Therapy Techniques You Can Use at Home
More Resources
Expert Clinicians
Get started today ->


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)











































































































































































































































































































































































































































.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




































































































































































































.jpg)


































































.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)






















































































.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


























.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

